

It is indisputable that the discovery of oil has dramatically changed human life. Oil dominates our daily life in several forms. However, at the same time, petroleum and its by-products have become a major threat to the environment.
Oil Spills involving tankers and rigs have polluted water bodies and badly affected the marine ecosystem. Over the last two centuries, a number of marine accidents have resulted in the spillage of millions of gallons of oil into our oceans.
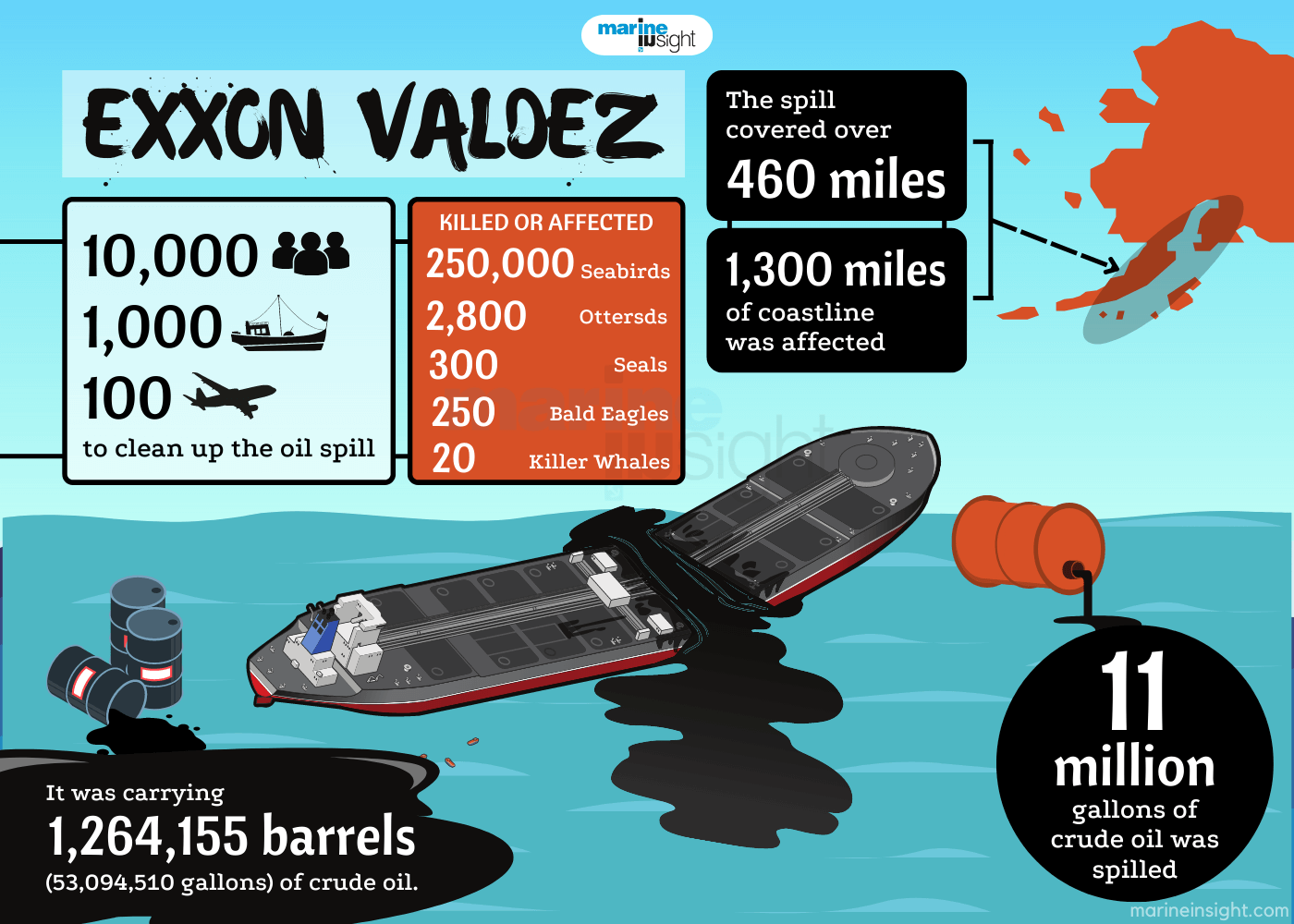
Among the oil spills that occurred in the last five decades, the Exxon Valdez Oil Spill remains the worst oil spill to date. In the accident that took place almost 30 years ago, over 11 million gallons of crude oil were released into the waters of the Gulf of Alaska, killing thousands of marine life.


It was on March 24, 1989, that the Exxon Valdez oil tanker struck the Bligh Reef in Alaska’s Prince William Sound region to begin one of the biggest maritime fatalities. Exxon Valdez, then owned by Exxon Shipping Company, was en route to Long Beach, California, from the Valdez Marine Terminal when it slammed into the reef at around 12 am local time.
The oil tanker Exxon Valdez was loaded with roughly 54 million gallons of oil of which 10.8 million gallons were released into the waters of Prince William Sound as the hull of the vessel was torn open in the accident. Exxon Valdez oil spill is considered to be the second major oil spill in the US after the Gulf of Mexico’s Deepwater Horizon oil spill.
The Exxon Valdez disaster led to the examination of oil spill prevention rules and regulations in the US. The 1990 Oil Pollution Act mandated that oil companies take greater precautions by operating double hull tankers and pay greater penalties in case of future oil spills. Apart from this, the Exxon Valdez Oil Spill Trustee Council was formed for the restoration of the marine habitats affected by accidents.


Various reports following the accident have identified a number of factors that made Exxon Valdez run aground on the reef under the command of Captain Joseph Hazelwood. It was reported that the captain was not at the helm of the tanker when it met with the accident on a route that is known for its navigational hazards.
According to reports, before handing over the ship’s control to the Third Mate, Hazelwood had apparently altered the vessel’s course to avoid icebergs. The Third Mate, unfortunately, failed to manoeuvre the vessel properly, and the vessel left the shipping lane to end up colliding with the reef, chiefly due to broken radar. In fact, the radar was not working for more than a year before the oil spill accident.
Further investigations also revealed that Hazelwood was under the influence of alcohol and he was asleep in his bunk during the accident. Investigators also pointed out that Hazelwood made a mistake by handing over the vessel’s helm to the sleep-deprived Third Mate, who was also not professionally qualified to take control of the vessel. The vessel also didn’t have sufficient crew abroad to perform the duties, further investigations revealed.
Moreover, authorities found that Exxon, like many other shipping companies, was not following measures that had been agreed upon, including the installation of iceberg monitoring equipment.
Reports also said the accident occurred as the ship took a route that was not prescribed under the normal shipping route. Because of this violation by the Exxon Valdez, owner Exxon Mobil charted out a clause which spoke about the strict following of the prescribed shipping routes and lanes so as to avoid any further marine accident of a magnitude like the Exxon Valdez Oil Spill.
After a year-long investigation and trial, Hazelwood was acquitted of being drunk during the voyage. However, the captain was convicted of misdemeanour negligence, fined $50,000, and sentenced to serve 1,000 hours of community service.
The collision of the supertanker with the reef ruptured 8 of its 11 cargo tanks, releasing 11 million gallons of crude oil-250,000 barrels into the waters of Prince William Sound, contaminating over 1,300 miles of coastline.
A delay in initiating cleanup made this accident catastrophic. The oil slick spread to more areas within days, making it no longer containable.
As the oil slick spread, marine wildlife was threatened. Marine mammals facing the threat of extinction because of the rise in temperatures had to deal with this human error.
Seabirds were forced to succumb to this disaster as the oil slick in the water trapped them to drown eventually. It is estimated that almost 250,000 seabirds, 2,800 sea otters, up to 300 harbour seals, 250 bald eagles, and at least 22 killer whales were killed.

The spill ended the lives of herring and salmon, and commercial fishing of crab, herring, rockfish, salmon, shrimp, etc. was closed in the area. Many were impacted financially, but its indirect impact was visible on fisheries.
There was a total financial loss of up to $580 million due to the reduction and in some areas, the complete absence of recreational fishing.
Tourism was also hampered, and the number of tourists who arrived in Alaska was at a record low for almost a year following the oil spill, making a significant impact on the local economy. According to reports, the oil spill affected more than 26,000 jobs in the tourism industry and over $2.4 billion in business.
And in spite of the fact that the company Exxon Mobil helped greatly in the clean-up operations along with the US Coast Guard, the inadvertent-yet-avertable accident caused by the Exxon Valdez ended up leaving a huge environmental impact.
Even years after the accident, the shoreline is yet to recover completely from the oil spill. The oil discharged from the Exxon Valdez still clogs the beaches in Alaska, the fishing industry that collapsed after the accident hasn’t recovered fully and the trauma it created among the fishing communities still remains- in the form of separated families and alcoholism.


The cleanup efforts were successful since the response to the incident was prompt not only by the US government but also by the company – Exxon Mobil.
Over 11,000 personnel, 58 air crafts, and 1,400 vessels were used to clear the affected area and it involved complex operations like relocating several marine creatures in order to safeguard their life till the clean-up operations were completed successfully.
The entire course of the clean-up operation took around three years, from 1989 to 1992 and even now, the area is being monitored by marine scientists.
According to reports, the shipping company spent more than $3.8 billion on the cleanup costs and also compensated 11,000 fishermen and others affected by the disaster.
The accident also followed a number of legal battles between the shipping company and the federal government as well as the Alaska fishermen’s union.
In 1994, Exxon was asked by an Alaskan court to pay $5 billion in punitive damages. However, after a number of appeals, the U.S. Supreme Court reduced the amount to $507.5 million. During the operation, the methods used for cleaning the oil included burning, mechanical cleanup, and the use of chemical dispersants.
Surface oil was cleared up to a larger extent, while the ‘sub-surface oil’ remained. It contains far more poisonous, and despite the clean-up, about 20 acres of the Alaskan coastline is polluted by sub-surface oil.
The enormity of the marine casualty caused by Exxon Valdez is something that is being felt even in recent times. But owing to the prompt and effective response from the concerned parties, the impact of the Exxon Valdez Oil Spill will definitely be reduced.
Owing to this positivity, one can rest assured that in spite of an accident happening, one managed to avert the worst and ended up doing a marine salvage in the best possible manner.
A small quantity of oil from the 1989 Exxon Valdez spill is found in patches below Prince William Sound, Alaska and its beaches. Although studies suggest, the remaining oil does not pose a significant threat to aquatic life.
No deaths were caused by the disaster, however, four people died during the cleanup operations.
After the incident, the ship returned to the San Diego shipyard where it was constructed. It was sold to a US-based company called Global Marketing Systems and then resold to Chinese Best Oasis. In 2012, it was dismantled in the Alang Shipbreaking yard in Gujarat, India.
The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) blamed the Exxon company, its overworked crew, inadequate safety measures and carelessness shown at sea.
Captain Hazlewood was fined $ 50,000 and had to give 1000 hours of community service. He was fired and later became a teacher at a maritime school. He also worked as a law consultant in New York later.
A marine ecosystem may take around 3 to 10 years to recover from an oil spill, depending on the accident’s severity.
Disclaimer: The authors’ views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect the views of The Marine Learners. Data and charts, if used, in the article have been sourced from available information and have not been authenticated by any statutory authority. The author and The Marine Learners do not claim it to be accurate nor accept any responsibility for the same. The views constitute only the opinions and do not constitute any guidelines or recommendation on any course of action to be followed by the reader.
The article or images cannot be reproduced, copied, shared or used in any form without the permission of the author and The Marine Learners.










We believe that knowledge is power, and we’re committed to empowering our readers with the information and resources they need to succeed in the merchant navy industry.
Whether you’re looking for advice on career planning, news and analysis, or just want to connect with other aspiring merchant navy applicants, The Marine Learners is the place to be.