

Cargo ships are classified into various types based on purpose, size, type of cargo etc.
The economic factor is of prime importance in designing a merchant ship. Every owner wants maximum return on their investment, which means a ship’s construction not only depends on the current economic necessities, but the factor of future adaptability also plays a part.
From the preliminary design of a vessel due for construction, the following information can be obtained:
A layout of the various ship types and their subdivisions will be listed, covering a wide range of all vessels in operation.
The type of ship plays an important role in deciding the above-mentioned parameters.
Related Read: What are Ship Prefixes for Naval and Merchant Vessels?
Ships are mainly classified into the following types:
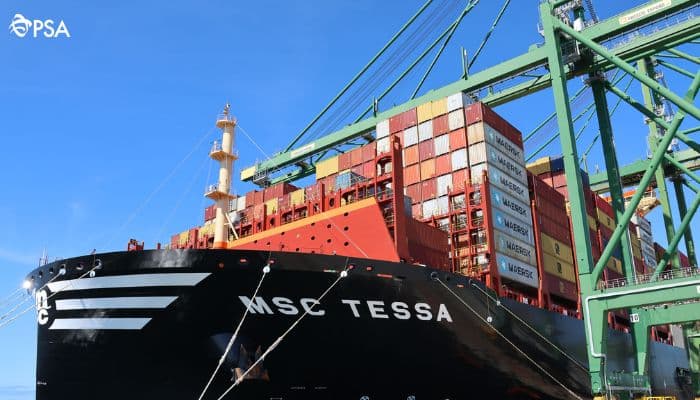
1. Container Ships
2. Bulk Carrier
3. Tanker Ships
4. Passenger Ships
5. Naval Ships
6. Offshore Ships
7. Special Purpose Ships
As the name suggests, a vessel structured specifically to hold huge quantities of cargo compacted in different types of containers is referred to as a container vessel (ship).
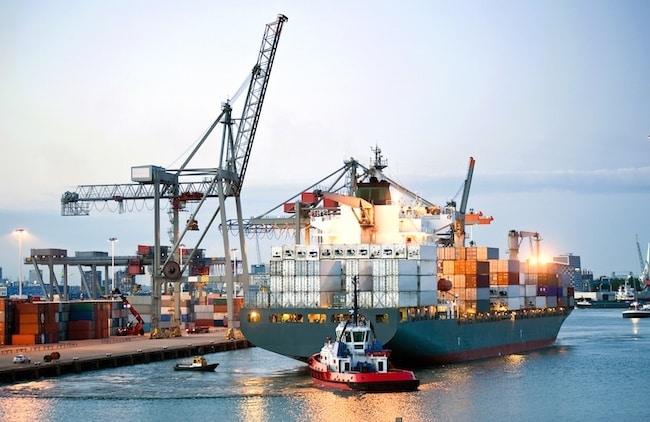


Types of Container Ships On Basis Of Sizes:
Learn about different types of container ships.
Refrigerated Container Ships: These Vessels carry refrigerated cargo (mainly in refrigerated containers)
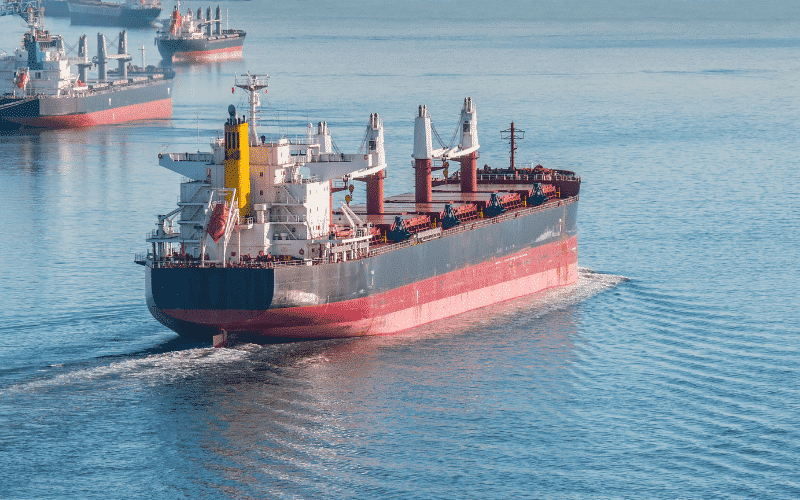


Read types of bulk carriers in detail here
Some other forms of dry cargo are:
Tanker ships are specialised vessels for carrying a large amount of liquid cargo. Tankers are further sub-divided into different types based on the cargo they carry.
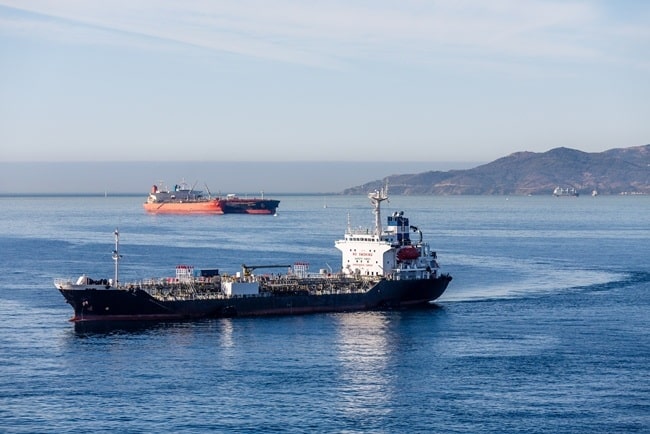


Read in detail – What are tanker ships?
The main types of tankers are:
Oil Tankers: Oil tankers mainly carry crude oil and its by-products.
Liquefied Gas Carriers: A gas carrier (or gas tanker) is designed to transport LPG, LNG or liquefied chemical gases in bulk.
Chemical and Product Carriers: A chemical tanker is a type of tanker ship designed to transport chemicals and different liquid products in bulk
Other types of tankers: Some other types of tankers are juice tankers, wine tankers, integrated tug barges etc.
Based on their size, tankers are further divided into various types such as:
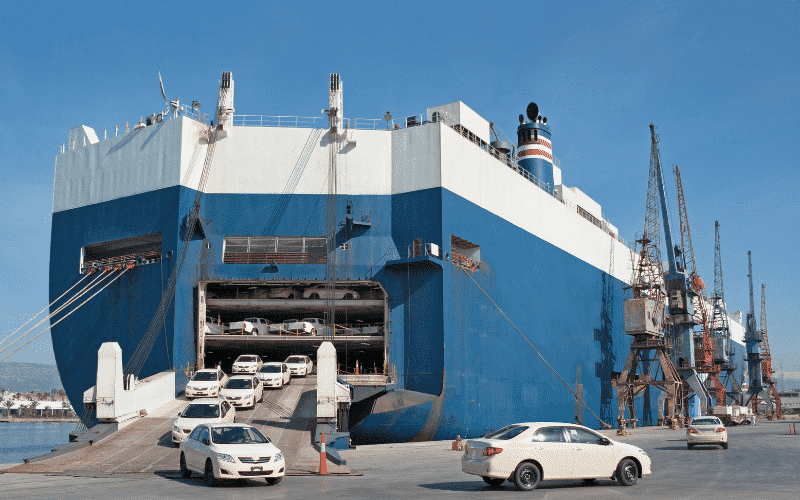


Passenger ships, as the name suggests, are mainly used for transiting passengers.
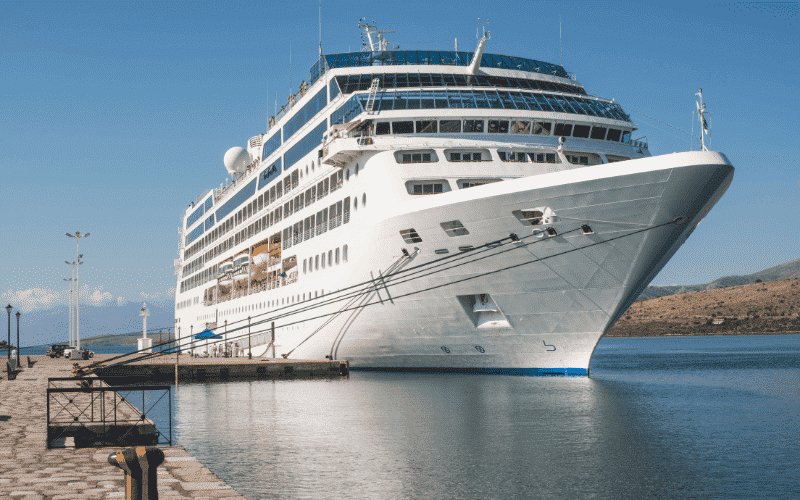


They are mainly classified into:
Ferries – Vessels used for transiting passengers (and vehicles) on short-distance routes are called ferries.
Cruise Ships – Mainly used for recreational activities, cruise ships are like luxurious floating hotels with state-of-the-art facilities.
They are further classified as:
Learn more about different types of passenger ships.
Offshore vessels mainly help in oil exploration and construction jobs at sea. Offshore vessels are of several types.
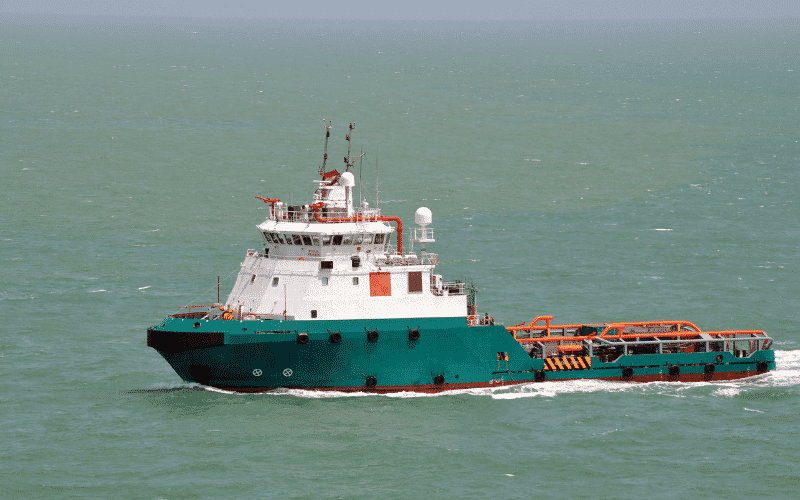


Some of the main ones are:
Learn more about different types of offshore vessels here.
Ships or boats used for recreational or commercial fishing at sea are called fishing vessels.
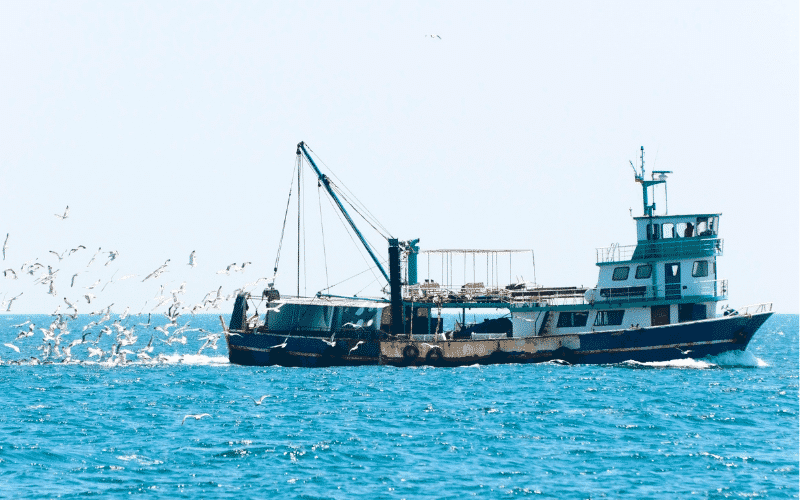


Fishing vessels are mainly classified into two types – trawlers and non-trawling vessels.
Learn more about types of fishing vessels here.
Speciality vessels are constructed and used for specific purposes.
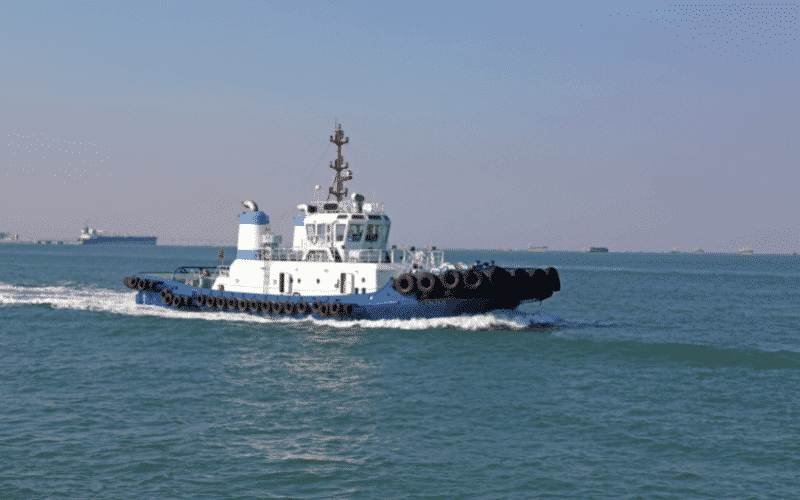


Tugs: A tug (tugboat) is a boat or ship that manoeuvres vessels by pushing or towing them.
Tenders – A boat or a larger ship used to service or support other boats or ships, generally to transport people and/or supplies, is called a tender vessel.
Pilot Crafts – Pilot crafts are used for the transportation of harbour pilots.
Cable Layers – Cable laying vessels help in laying cables onto the sea bed.
Research Vessels – They are special types of vessels used to carry out a variety of research at sea. Some of the most common types of research vessels are – seismic vessels, hydrographic vessels, oceanographic vessels, polar vessels etc.
Related Read: 12 Noteworthy Research Vessels
Salvage Vessels – Salvage vessels are vessels engaged in salvage operation; recovery of lost property at sea.
Lightships: A light vessel, or lightship, is a ship that acts as a lighthouse. They are used in waters that are too deep or otherwise unsuitable for lighthouse construction.
Barge Carriers: A barge is a flat-bottomed boat built mainly for river and canal transport of heavy goods.
Timber Carriers: Vessels that carry timber
Livestock Carriers: Vessels that carry livestock/animals
Ice breaker ships: They are used for cutting ice deposits in extremely cold climate conditions to make waters navigational.
Related Read: What is an Ice Breaker Ship?
High-speed crafts are a special type of technologically advanced high-performance (typically high speed) marine vehicles. Though most of these technologies are not used in commercial vessels, a few have been successfully implemented and tested in conventional merchant vessels of small scale.
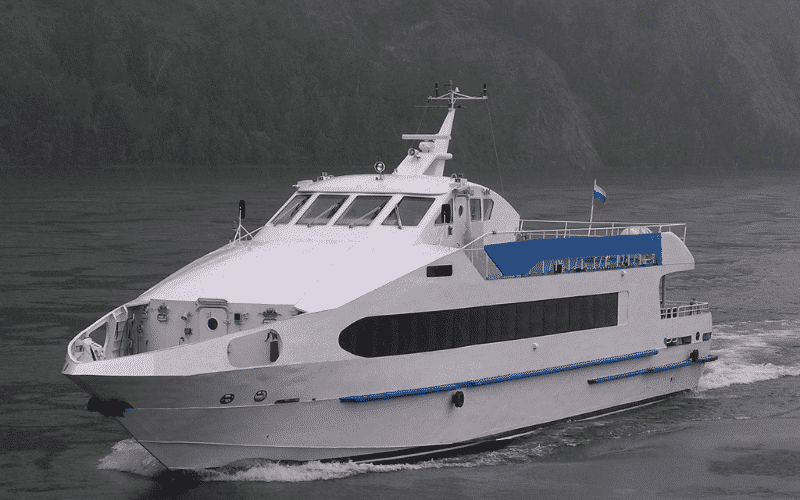

Some of the main types of high-speed crafts are:
Learn more about different types of high-speed crafts.
Dredging is an excavation activity usually carried out underwater, in shallow seas or freshwater areas, to gather up bottom sediments and widen.
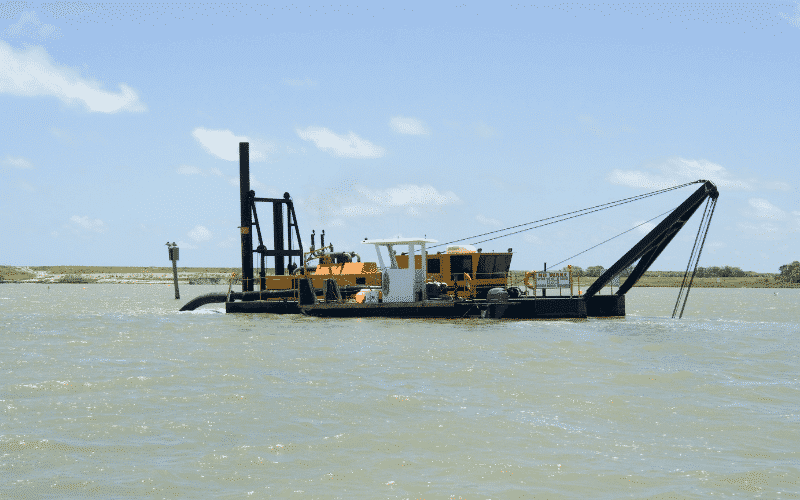

Dredgers are vessels with excavation tools used for removing sand and other types of deposits from the seabed. Dredgers are used for several purposes, such as making shallow coastal areas navigational, deep-sea mining etc.
Dredgers are mainly classified into two types:
Learn in detail about different types of dredgers.
You might also like to read:
Disclaimer: The authors’ views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect the views of The Marine Learners. Data and charts, if used in the article, have been sourced from available information and have not been authenticated by any statutory authority. The author and The Marine Learners do not claim it to be accurate nor accept any responsibility. The views constitute only the opinions and do not constitute any guidelines or recommendations on any course of action to be followed by the reader.
The article or images cannot be reproduced, copied, shared or used in any form without the permission of the author and The Marine Learners.










We believe that knowledge is power, and we’re committed to empowering our readers with the information and resources they need to succeed in the merchant navy industry.
Whether you’re looking for advice on career planning, news and analysis, or just want to connect with other aspiring merchant navy applicants, The Marine Learners is the place to be.