

I still remember the day when I joined my maiden vessel more than a decade ago. A Supramax bulk carrier with the least automation and the most troubles. I was welcomed by a lot of judgemental yet uncaring eyes.
A new Cadet is on board! To add some spice to it, he’s a first-timer and presumably stupid; An old and tough Soviet Chief Officer who’s pissed because he couldn’t sign off in the last port.
Rain poured down the sky, and the day couldn’t get gloomier beyond imagination. I was shown my cabin and asked to change and to report immediately to the Training officer, who didn’t give a damn about who or where the trainee was. Without looking at me, he asked me to take the sounding of the tanks using a sounding rod tied to a rope, already drenched in the water. If a nightmare is a reality, this is it. With no one to supervise or demonstrate, I somehow could give the approximate sounding of the ballast tank I was asked to check.


Next, after the sounding, “Go do the line setting of the Forepeak tank in the Engine room”. Setting the lines was a far-off fantasy, and I didn’t even know the way to the Engine Room. Yeah, those were the days, and such were the challenges in those days. Yes, if you ask today’s Chief officers who were cadets or junior officers, then they would undoubtedly say, “Those were the days”. The primary concern in port operations was Cargo, and the junior officers and cadets would take care of the Ballast operations (mostly).
Today, as a Chief officer and the Ballast water management officer, I face other distinct challenges if we talk about Ballast operations.


It isn’t the case that we didn’t think about the environment back then. To prevent the transfer or introduction of pathogens or aquatic organisms from the source port State to the destination port State, IMO laid down guidelines for the implementation of Ballast water management and Sediment control on board ships in the form of the International Convention for the Control and Management of Ship’s Ballast Water and Sediments (BWM Convention), which was adopted in 2004 and entered into force on 8th Sept 2017. The purpose of the Ballast Water management system is to minimise the risk of transplanting harmful aquatic organisms and pathogens from the ship’s ballast water and associated sediments.
There are broadly two ways in which we can comply with the regulations.
First is the conventional Ballast Water exchange, and the other is the Ballast Water treatment system.
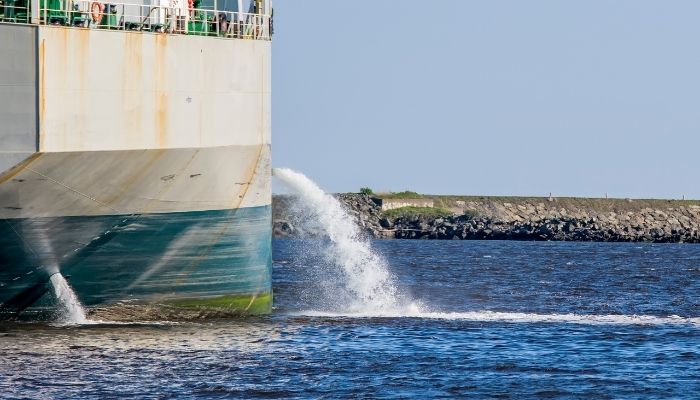
The former has been in practice through ages and is carried out in three ways:
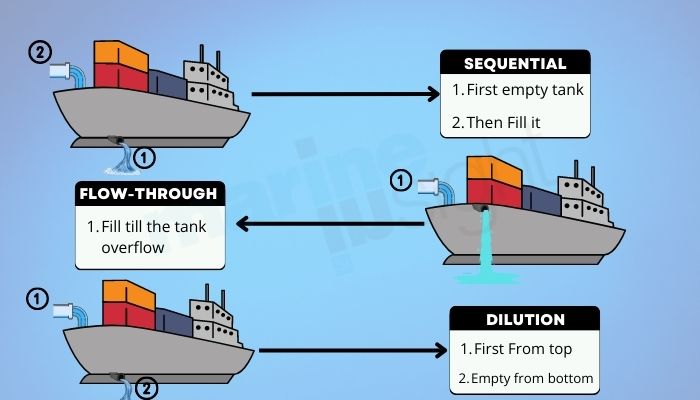

The Ballast Water Convention requires that the vessel should conduct ballast water exchange :
At least 200 nm from the nearest land and in water at least 200m in depth; if this is not possible, then as far as possible from the nearest land, and in all cases, at least 50nm from the nearest land and in water at least 200m in depth, or sea areas designated by the port state.
The standards mentioned above are categorised in the D-1 Standard of Ballast Water Management.
Now let’s talk about the elephant in the room, the Ballast Water Treatment system.
As per the regulations laid down in the BWM Convention,
Any type of approved ballast water treatment system shall discharge :
Capacity discharge for organisms:
BWTS must have a type approval certificate and must be approved by the Administration.
The aforementioned standards constitute the D-2 Standard of Ballast Water Management.
So, the ships with the Ballast Water Management system complying with both the D-1 and D-2 standards can carry out the Ballast Water Exchange and can also use the Ballast Water Treatment system. On the other hand, if a ship complies only with the D-2 standards, she can only use the BWTS for ballast operations and is therefore not allowed to carry out Ballast Water Exchange.
However, there are a few exceptions ( Such as the Safety of the Ship in Emergency situations, Accidental discharge, for the purpose of avoiding pollution incidents, etc.)
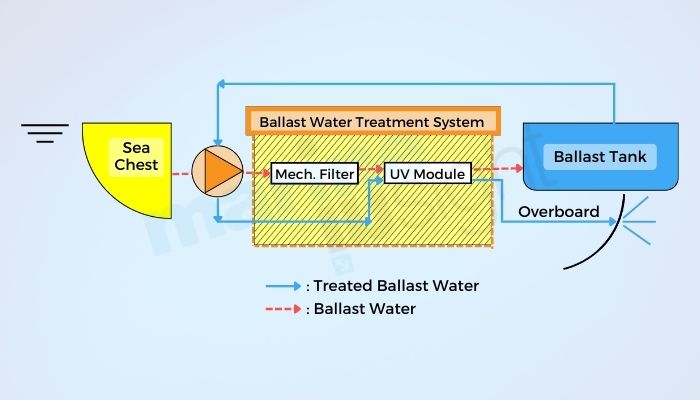
A water filter is normally used in conjunction with another method, such as the ones discussed below. First, filters help to remove sediment, which can be taken in at turbulent ports and, if not properly removed, can accumulate in the ballast tanks. Also, a filter can remove a substantial portion of the micro-organisms. This reduces the time and energy required to neutralise the organisms that may enter through the filter and therefore need to be treated before the water they live in can be stored on board or dumped.
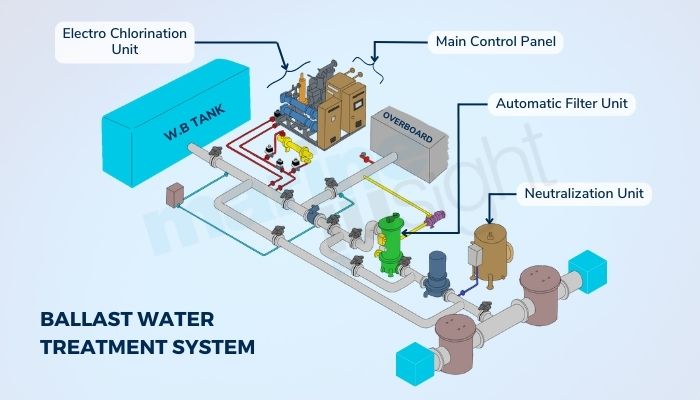
The most widely used methods are the UV system, the Chemical treatment system and the Ultrasonic system. I have only encountered the UV system BWTS, and the ones who have seen the other systems vouch for the fact that the UV system is one of the most effective and hassle-free systems to be used. We’ll discuss the UV BWTS system further.

The first and foremost concern which I personally feel as a seafarer and the Ballast Water Management Officer is that when any regulation is formulated and enforced by the IMO or other concerned Organization, does it take into consideration the factors which are not in the control of the entities directly affected by that regulation or convention. For e.g., We as seafarers are duty-bound to comply fully with the provisions of the Ballast Water Management System but is the Port State in which the vessel is operating in any way accountable for the fulfilment of that regulation?
Ignoring for a while the issues faced because of the substandard quality of the components of the BWTS system or the untimely breakdown of the BWTS system, the exposure of the vessel to the heavily turbid or muddy waters in the port where the vessel is berthed is a major issue. As a Chief officer, my primary concern is whether I would be able to ballast even half of the quantity I’ve planned to.
And if you push it further and stress the system, the filter gets choked ( in one case, the filter element suffered serious damage ), and the system gives away. Time in such cases becomes crucial because stoppage of the cargo operations from the vessel’s side for ballast operations can create a lot of ruckus, commercial losses and intense cross-questioning from the stakeholders.

The eventual decision that can be taken in such conditions is to take dispensation from the Flag State and, provided the Flag State approves, ballast the tanks with the muddy water and later carry out the Ballast Water Exchange or deballast to the shore reception facilities if in case the terminal accepts that.
This will mainly be required if the vessel unloads the cargo in a single port. Suppose in case the ship is partly unloading cargo and would require minimum or no ballast and already has some ballast water in her tanks. In that case, the ship might consider doing the internal transfer of the existing treated ballast water to correct the list/trim for the cargo operations, depart after carrying out the operations, and when in the open sea or a relatively clean source of water, take in the required quantity of ballast.
Moreover, the company might not always be punctual and efficient in the supply of spares or replacement parts. Notwithstanding the fact that the makers might take a lot of time supplying the ordered part, these parts are costly, and the company doesn’t always supply you with everything you ask for. A part was ordered before I joined that particular vessel, and the part was not received even after I signed off from that vessel. So, the readers are left to the imagination here.
Another major issue which I faced was the overheating of the Ballast sensor panels and circuits in the BWTS room, especially in the relatively warmer / hot regions of the world. Irrespective of the fact that the ventilation/cooling/exhaust fans are provided in the panels, they are rendered ineffective in such a hot climate.
This leads to repeated alarms in the BWTS system and subsequent breakdown/trip of the BWTS system. The thing that can be done in such cases is to deploy an intrinsically safe (on tankers especially) portable fan in the BWTS room and open all the doors/hatches/vents/openings of the BWTS room for proper ventilation. Well, the other thing that can be done is to pray that your BWTS system copes up.
On the flip side, you can’t bypass the system because then you’d be deemed to be going against the regulations. We’re left with limited choices and immense stress and pressure in such situations, and then I wonder, did the IMO even take the muddy water into consideration before drafting the relevant regulation? We’re duty-bound to comply with the regulations in whatsoever conditions (except in life-threatening situations and emergencies), and the conditions which might totally turn against us.
The problems frequently faced during the BWTS systems include, but are not limited to :
The consequence of a treatment system failing to perform as anticipated is a regulatory violation picked up by Port State control (PSC) during an inspection. The penalisation depends on the jurisdiction, but the expected outcome could be PSC deficiencies, detentions and financial penalties.
Even giants such as Intertanko and ABS have acknowledged that Operational problems continue with Ballast Water Treatment Systems. The degree of operational challenges with BWTS fitted by tanker owners (mostly retrofit) was revealed by Intertanko at a forum in Singapore. The feedback from the members was that in their assessment, 60% – 80% of systems did not work correctly.
Consequently, today a part of me puts more focus on the BWTS operation than the Cargo operation, majorly because the former has become more challenging in the port operations. The failure of the BWTS system in critical stages could be nerve-wracking. On a candid note, the BWTS system gives me and the electrician sleepless nights. On a serious note, compliance with the Rest hours has become a myth. Never had I imagined that there would come a day when we would need to treat the Ballast water. Inevitably, the day came and came with a lot of concerns.
You might also like to read-
Disclaimer: The authors’ views expressed in this article do not necessarily reflect the views of The Marine Learners. Data and charts, if used, in the article have been sourced from available information and have not been authenticated by any statutory authority. The author and The Marine Learners do not claim it to be accurate nor accept any responsibility for the same. The views constitute only the opinions and do not constitute any guidelines or recommendations on any course of action to be followed by the reader.
The article or images cannot be reproduced, copied, shared, or used in any form without the permission of the author and The Marine Learners.










We believe that knowledge is power, and we’re committed to empowering our readers with the information and resources they need to succeed in the merchant navy industry.
Whether you’re looking for advice on career planning, news and analysis, or just want to connect with other aspiring merchant navy applicants, The Marine Learners is the place to be.